Learn Narration Change Rules in 5 Easy Steps with Example
Many of you face problems changing Narration and many don’t even know about this. I’m going to share 5 very simple tricks to change narration with example. You can learn narration change rules in Bangali…
Many of you face problems changing Narration and many don’t even know about this. I’m going to share 5 very simple tricks to change narration with example. You can learn narration change rules in Bangali too.
I hope, you will find no difficulties to change direct speech to indirect speech after this lesson.
আপনি হয়তো জানেন না, Narration কি। কোন ব্যপার না এই টিউটোরিয়াল এর পর আপনি 100% বুঝে ফেলতে পারবেন।
Idea about Narration
Think, yesterday your father told you, “I am reading news.” This bold sentence is a direct speech.
Today, If you tell your mother what your father said yesterday, you will say: Father said that he was reading news.
This bold sentence is an example of indirect narration.
ভাবুন, আপনার বাবা গতকাল আপনাকে বলল, “আমি সংবাদ পড়ছি”। এটি Direct
আবার, আজ আপনি কথাটি আপনার মাকে গিয়ে কিভাবে বলবেন? বলবেন, বাবা বললেন যে তিনি সংবাদ পড়ছিলেন। এটি Indirect.
এখানে, আপনি আপনার মত করে, আপনার বাবার বলা বাক্যটি পরিবর্তন করেছেন। এমন পরিবর্তন করাই হচ্ছে, Direct থেকে Indirect Speech এ পরিবর্তন করা।
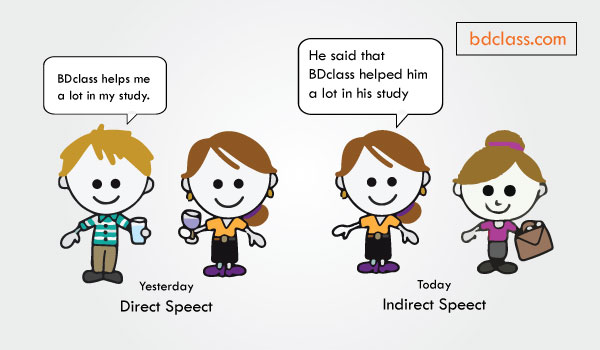
ছবিটি দেখুন, একটি ছেলে তার মেয়ে ক্লাসমেটকে গতকাল বলেছিল, “BDclass helps me a lot in my study” অর্থাৎ বিডিক্লাস তাকে পড়াশুনায় অনেক সাহায্য করে।
পরের অংশে, মেয়েটি তার অন্য বন্ধুকে গতকালের ঘটনাটি আজকে বর্ণনা করছে, “He said that Bdclass helped him a lot in his study”
এখানে, মেয়েটি যে গতকালের ঘটনাটি অন্য বন্ধুর নিকট বর্ণনা করছে এটাকে বলে Reporting. অর্থাৎ এখানে মেয়েটি গতকালের ঘটনাটি আজ অন্যজনের কাছে Report করছে।
এই Reporting করার সময়, গতকালের বন্ধুর বলা বাক্যটি “BDclass helps me a lot in my study” পরিবর্তন হয়ে “Bdclass helped him a lot in his study” হয়েছে।
এমন পরিবর্তনকে আমরা বলি, Narration Change বা উক্তি পরিবর্তন। এই লেসনে আমরা শিখব কিভাবে বিভিন্ন ধরণের বাক্যের Narration পরিবর্তন করতে হয়।
Narration সম্পর্কে বাংলায় আরো বিস্তারিত জানতে পড়ুন What is Narration
How to Change Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
Now we should know how to change these speeches from direct to indirect.
When we make an indirect speech, we need to change a few things Tense, Type of Sentence, Pronouns, Adverbs and Demonstratives, and Modals.
I will be sharing Narration Rules with Example. So, follow them attentively.
1. Changing Tense
At first, you should learn how to change the tense of direct speech. There is 2 Parts in the sentences, Reporting Verb, and Reported Speech.

Rule: When the Reporting Verb is Past Tense, Only then we have to change the Tense of Reported Speech. You need not change Tense if Reporting Verb is Present or Future Tense.
যখন, Reporting Verb Past Tense হয়, শুধুমাত্র তখনই Reported Speech এর Tense পরিবর্তন হবে।
Reporting Verb যদি Present বা Future হলে Tense পরিবর্তন করতে হবেনা।
Example 1:
Direct: She said, “We work for New York Times.” [Reporting verb is Past Tense]
Indirect: She said that they worked for New York Times. [work changed to Past tense ‘worked’]
Example 2:
Direct: She says, “We work for New York Times.” [Reporting verb is Present Tense]
Indirect: She says that they work for New York Times. [Work remained the same tense]
Usually, Present Tense changes to Past Tense. See the table below,
| Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|
| Present Indefinite | Past Indefinite |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Present Perfect | Past Perfect |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
Past Tense changes to Past Perfect Tense. See the table attentively
| Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|
| Past Indefinite | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past Perfect | No change |
| Past Perfect Continuous | No change |
Exceptional Rule: If the reported speech is still true or happening or habitual and scientific truth, we do not need to change the tense in the reported speech. See the following example.
Reported Speech এর ঘটনাটি যদি বাস্তবিকভাবে বা বিজ্ঞানসম্মতভাবে সত্য হয়ে থাকে, আপনাকে এর Tense পরিবর্তন করতে হবেনা, তবে Pronoun ও Verb এর রুপ পরিবর্তন হতে পারে।
Example 3:
Direct: She said, “I live in Dhaka.” [She is currently living in Dhaka]
Indirect: She said that she lives in Dhaka. [Tense is not changed]
2. Pronoun Change
Pronouns in Direct Speech, will be changed in Indirect Speech according to the speaker, the listener or any third person.
Direct Speech এ Speaker (বক্তা) এবং কাকে বুঝাচ্ছে, তার উপর ভিত্তি করে, Direct Speech এর Pronoun গুলো Indirect Speech এ পরিবর্তন হবে। যা, আপনি ইতোমধ্যে Idea about Narration অংশে বুঝতে পেরেছেন।
Direct: Hasan said, “I cannot be with you.”
Indirect: Hasan said that he could not be with me.
Direct: They said, “We will join a party tonight.”
Indirect: They said that they would join a party that night.
Direct: I told Rina, “You should stay.”
Indirect: I told Rina that she should stay.
Direct: She asked me, “How are you doing today?”
Indirect: She asked me how I was doing that day.
Direct: Robert said, “Can you pull me up?”
Indirect: Robert asked if I could pull him up.
3. Types of Sentence
We know there are 5 types of sentences (assertive, interrogative, imperative, optative, and exclamatory). All these 5 types of sentences will change into Assertive Sentence in Indirect Speech.
How you will change different types of sentences in Indirect Speech, see below;
i) Assertive Sentence

The reporting verb will be “said” with no object, “told” with an object. For 2nd time, you can use “added” instead of “said”.
The comma (,) and inverted comma (“”) will be removed and we’ll use “that”. Tense, Pronoun, and Adverbs in reported speech will change according to the meaning.
Follow the example for better understand;
Direct: Jim said, “Bill loves to drink Wine.”
Indirect: Jim said that Bill loved to drink Wine.
Direct: Munni said to Rumi, “I will be waiting for you.”
Indirect: Munni told Rumi that she would be waiting for her.
ii) Interrogative Sentence

For interrogative sentences, the reporting verb “said” will be changed to “asked/ inquired/ wanted to know”
Remove the comma (,) and inverted comma (“”) and use “if/whether”. When the interrogative sentence has a WH word (What, Which, When, Where, How), use that WH word.
Tense, Pronoun, and Adverbs in reported speech will change according to the meaning.
Follow the example for better understand;
Example 1:
Direct: Rocky said, “Who will come with me?”
Indirect: Rocky asked who would go with him.
এখানে প্রশ্নবোধক বাক্যের কারণে, said পরিবর্তন হয়ে asked ব্যবহার হয়েছে। আবার, Reported Speech এর প্রশ্নটি Who (WH) word দ্বারা শুরু হয়েছে, তাই (, “”)-র পরিবর্তে who দ্বারা ২টি বাক্যকে যুক্ত করা হয়েছে। এবং খেয়াল করে দেখুন, প্রশ্নবোধক বাক্যটি সাধারণ বাক্যে পরিবর্তন করা হয়েছে।
Example 2:
Direct: Tom said to me, “Are you from Bangladesh?”
Indirect: Tom asked me if I was from Bangladesh.
এখানে Reported Speech এর প্রশ্নে কোন (WH) word নাই, তাই (, “”)-র পরিবর্তে (if/whether) দ্বারা ২টি বাক্যকে যুক্ত করা হয়েছে।
Example 3:
Direct: Mother said, “How is the chicken?”
Indirect: Mother asked me how the chicken was.
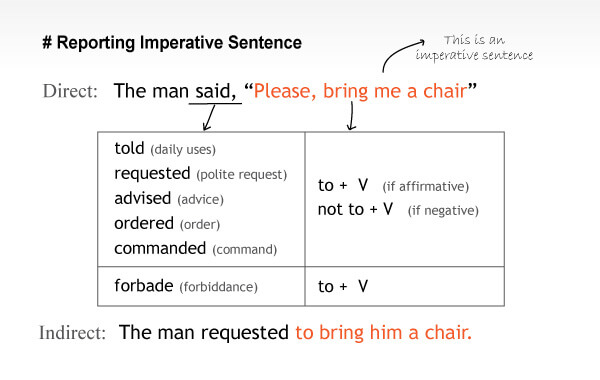
iii) Imperative Sentence
Use reporting verb (tell/request/advise/order/forbide/command) according to the reported speech. We often use “tell” with an infinitive “to+verb” while reporting imperatives.
Use (told) for daily conversation, (requested) for request, (advised) for advice, (ordered) for an order, (forbade) for forbiddance. (নিষেধ)
Then, add (to/not to) before the Verb of reported speech. Please see the following example for better understanding.
Reported speech এর ধরন অনুসারে Reporting verb (tell/request/advise/order/command) ব্যবহার হবে।
যদি Imperative sentence টি দৈনন্দিন কথোপকথন হয়ে থাকে Tell ব্যবহার করা যায়। অনুরোধ বুঝালে, Request, উপদেশের ক্ষেত্রে Advise, আদেশসূচক বাক্যের ক্ষেত্রে Order ও নিষেধ বুঝালে Forbid ব্যবহার করতে হবে।
এরপর, Reported speech এর Verb এর আগে (to/not to) বসবে এবং বাক্যের বাকি অংশ বসবে। উপরের ছবিতে একটু লক্ষ্য করলেই আপনি বুঝতে পারবেন।
Example 1:
Direct: Mother said to me, “Listen to your elders.” [This is an advice]
Indirect: Mother advised me to listen to my elders.
Example 2:
Direct: Mr. Kamrul said, “Don’t go near the house.”
Indirect: Mr. Kamrul forbade to go near the house.
Forbid এর অর্থ নিষেধ/ মানা করা যা নাবোধক অর্থ প্রকাশ করে, তাই এক্ষেত্রে (not to + verb) না হয়ে (to+verb) হবে।
যদি, এখানে “Forbid” ব্যবহার না করে “Tell” ব্যবহার করা হত,
Indirect: Mr. Kamrul told not to go near the house.
Example 3:
Direct: The old man said, “Please give me some food.”
Indirect: The old man requested politely to give him some food.
এখানে বাক্যটি একটি অনুরোধ, তাই “Request” ব্যবহার করা হয়েছে। আবার, “Please” দ্বারা বিনয় (politeness) বুঝানো হচ্ছে, তাই Requested এর পর Politely লেখা হয়েছে।
Imperative Sentences with ‘Let us/ Let’s’
আমরা সহ কোন কাজ সম্পাদন করব বা করার জন্য পরামর্শ/ প্রস্তাব দিতে, ‘Let us’ ব্যবহার করি।
যেমন, Let us play cricket “চলো আমরা মিলে ক্রিকেট খেলি” এ ধরণের বাক্যের উক্তি পরিবর্তন কিভাবে করবো দেখা যাক।
Said এর পরিবর্তে “proposed/suggested” ব্যবহার হবে। Reported speech কে যুক্ত করার জন্য “that” এবং এর পূর্বে “should/ might” বসবে।
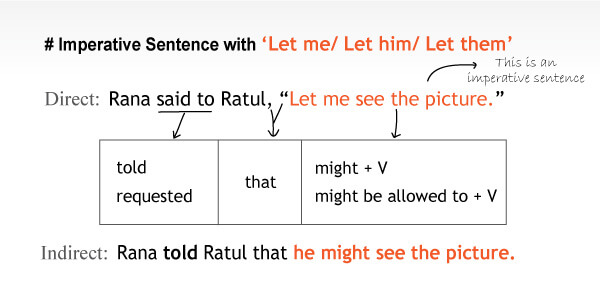
Imperative Sentences with ‘Let me/ Let him/ Let them’
আমাকে করতে দাও, তাকে করতে দাও এমন অনুরোধ করতে, ‘Let me, Let him, Let them. Let her’ ব্যবহার করি।
যেমন, Let me tell something. “আমাকে কিছু বলতে দাও” এ ধরণের বাক্যের উক্তি পরিবর্তন কিভাবে করবো দেখা যাক।
Said এর পরিবর্তে “told/requested” ব্যবহার হবে। Reported speech কে যুক্ত করার জন্য “that” এবং এর পূর্বে “might” বসবে।
iv) Optative Sentence

The reporting verb ‘said/said to’ changes to ‘wish/prayed’. The comma (,) and inverted comma (“”) will be removed and we’ll use ‘that’.
‘May’ will change to ‘Might’ and will sit before the verb.
Optative Sentence এ Reporting Verb হিসেবে ‘wish’ ব্যবহৃত হবে। যদি আল্লাহর কাছে কোন প্রার্থনা করা হয়, তখন prayed ব্যবহার করা যায়। এছাড়া, Reported Speech কে সংযুক্ত করার জন্য কমার পরিবর্তে ‘that’ বসবে
Follow the example for better understand;
Direct: Mother said to me, “May you be happy in your life.”
Indirect: Mother wished me that I might be happy in my life.
Direct: The teacher said to Rumi, “May you get GPA 5 in HSC exam.”
Indirect: The teacher wished Rumi that she might get GPA 5 in HSC exam.
Direct: Father said to Kiron, “May Allah help you.”
Indirect: The teacher prayed that Allah might help Kiron.
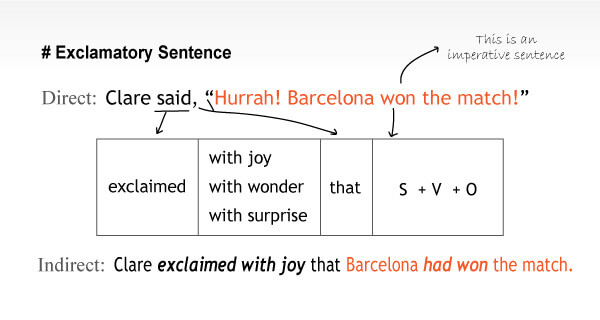
iv) Exclamatory Sentence
Follow the example for better understanding;
Direct: I said, “Alas! My pet died.”
Indirect: I exclaimed with sorrow that my pet had died.
Direct: The man said, “How fine the bird is!”
Indirect: The man exclaimed with surprise that the bird was very fine.
Direct: I said to her, “What a nice girl you are!”
Indirect: I exclaimed that she was a very nice girl.